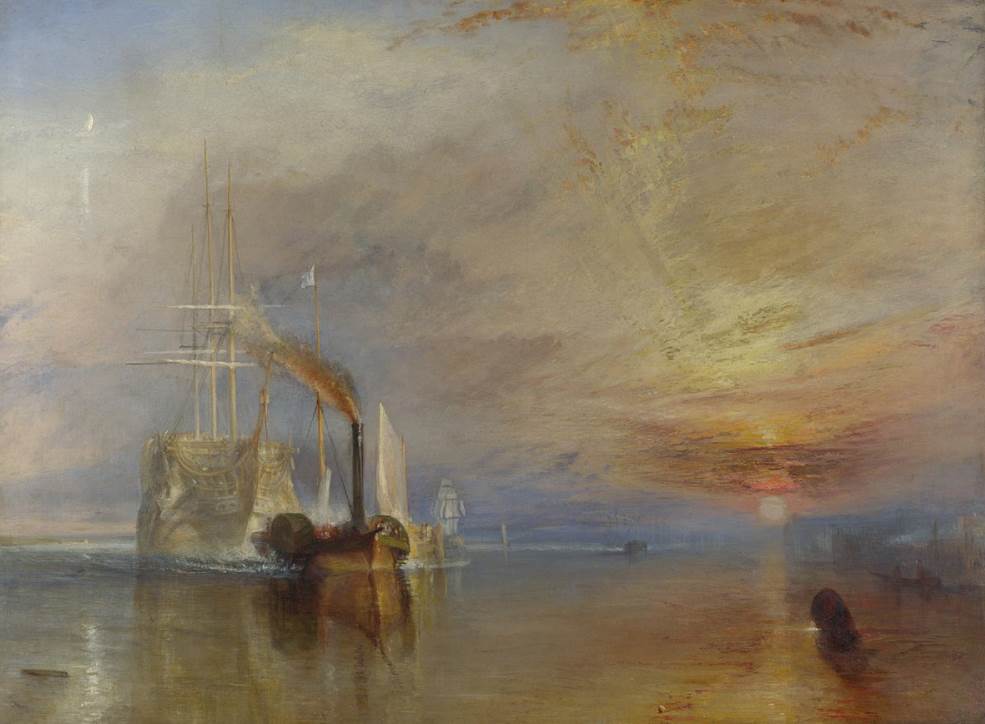The 18th century was marked by a drastic turn from Rococo art to Neoclassical art. These two art movements were opposites as one focused on curving frivolity while the other emphasized geometric harmony.
Another art movement emerged in the late 18th century called Romanticism and in this article, we’ll take a closer look at its history related to visual arts and what defines it.

History of Romantic Art
The first Romantic artists in the visual arts emerged in Germany and England and mainly focused on landscape paintings.
Caspar David Friedrich (1774-1840) and J.M.W. Turner (1775-1851) were born in the 1770s and took this type of genre to another level.
The history of Romanticism is defined as a reaction to both the Age of Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution. Artists countered the scientific approach to nature and often included a sense of nostalgia for simpler times.
The Neoclassical artists very much dominated the scene in France so it took a bit longer for Romanticism to emerge.
Some of the most notable Romantic artists were French, however, including Théodore Géricault (1791-1824) and Eugène Delacroix (1798-1863).
In Spain, the tragic events of the Peninsular Wars were magnificently captured by Francisco Goya (1746-1828), a man who became one of the first anti-war painters in history.
The movement started around 1800 and lasted until 1850 when it was replaced by the Realism movement and later Impressionism and Post-Impressionism.

Main characteristics of Romantic Art
The main goal of Romantic artists was to evoke a sense of emotion in viewers. Romantic art forces you to think with your heart instead of your brain.
The Rococo era mainly focused on trivial pleasures and hedonism and Neoclassical artists completely discarded these things.
When it comes to visual arts, Romantic Art can be defined by the following characteristics:
- High emphasis on emotions – The artists aimed to integrate a sense of awe, horror, terror, and fear into their art.
- Exaggerated drama – Many Romantic artists purposely increased the drama in their art to get their emotional message across.
- Mysticism – Some artists were so keen on expressing their personal emotions that their art became borderline mystical.
- Individualism – The artists were free to express their own emotions in their works as opposed to what was expected.
- Balance of thought and observation – Figures contemplating the vast natural landscape in front of them form a unity between thought and what can be observed.

Types of Romantic Art
Although Romanticism can be classified as an art movement, its scope was much more radical than that. It was both an artistic and intellectual movement that aimed to put the individual first.
The French Revolution played a major role in the development of Romantic artists because many were considered to be cultural revolutionaries themselves.
Below I have listed several manifestations of this sudden feeling that going against the conventional ideals in the world of art was possible.
Painting
The most notable representatives of the Romantic art movement in the visual arts were painters. This ranged from landscape painters in England and Germany to historical painters who used painting as a way to express political statements in France.
Sculpture
There were a couple of sculptors who embraced the Romantic art movement, including François Rude who worked on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris, Rudolf Maison, and Auguste Préault. Romantic sculptors often combined Neoclassical elements with emotional elements.
Architecture
Just like Romantic art, Romantic architecture was a reaction against the inflexible approach of Neoclassical architecture. This free approach to the design of buildings was combined with a sense of nostalgia which had the aim of evoking an emotional reaction.
Literature
Romanticism was highly influential in the world of literature. Some of the most famous authors and poets in history emerged during this era, including Edgar Allen Poe, Walter Scott, Lord Byron, and William Blake. Human psychology and the supernatural often played a major role in Romantic novels and poems.

Notable Romantic Artworks
To fully understand Romanticism, there’s no better way than to discover some of the most notable artworks that were produced during this art movement. Below is a list of paintings that define the Romantic era.
- Wanderer Above the Sea Fog (1818) – The ultimate masterpiece by Caspar David Friedrich which has become the ultimate icon of the Romantic art movement.
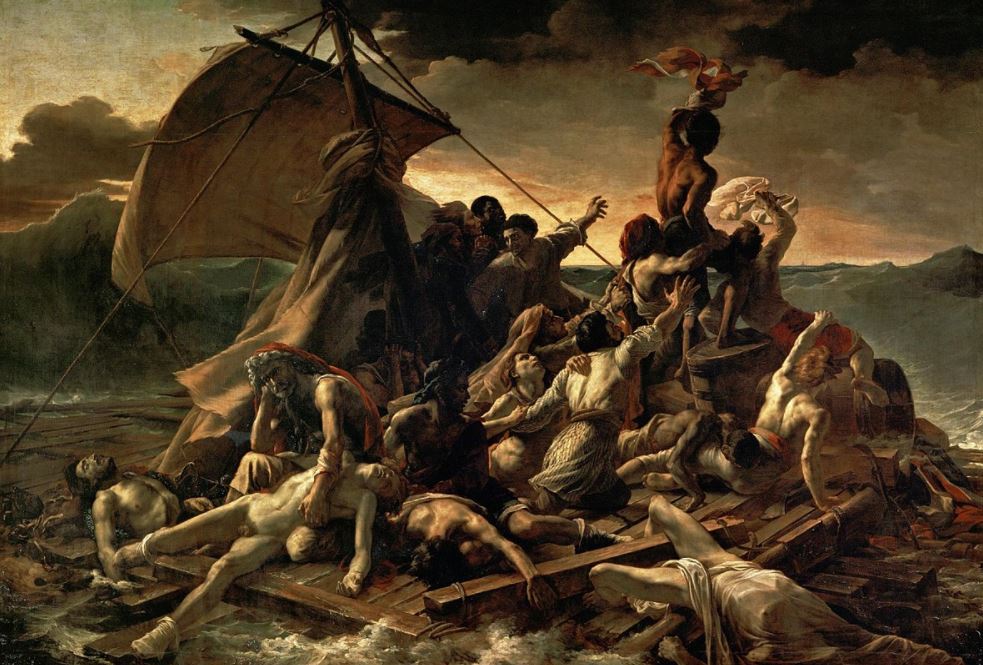
- The Raft of the Medusa (1819) – One of the first major and highly influential expressions of the Romantic movement in France, painted by Théodore Géricault.
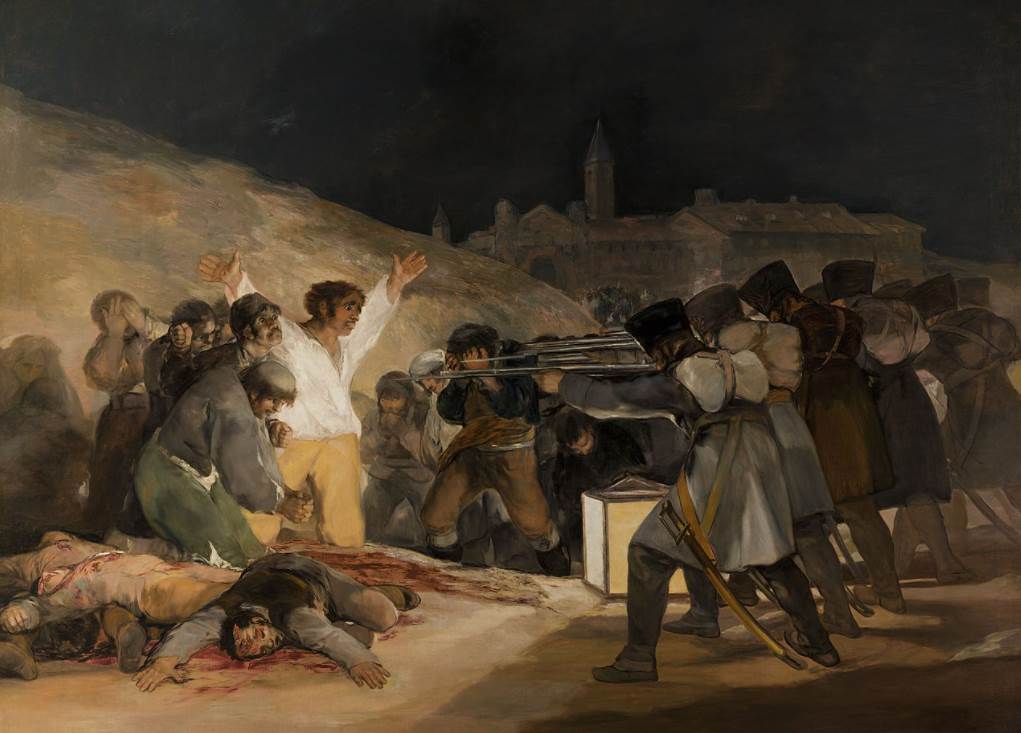
- The Third of May 1808 (1814) – One of the most famous works by Francisco Goya and arguably the first painting in history that depicts the horrors of war.
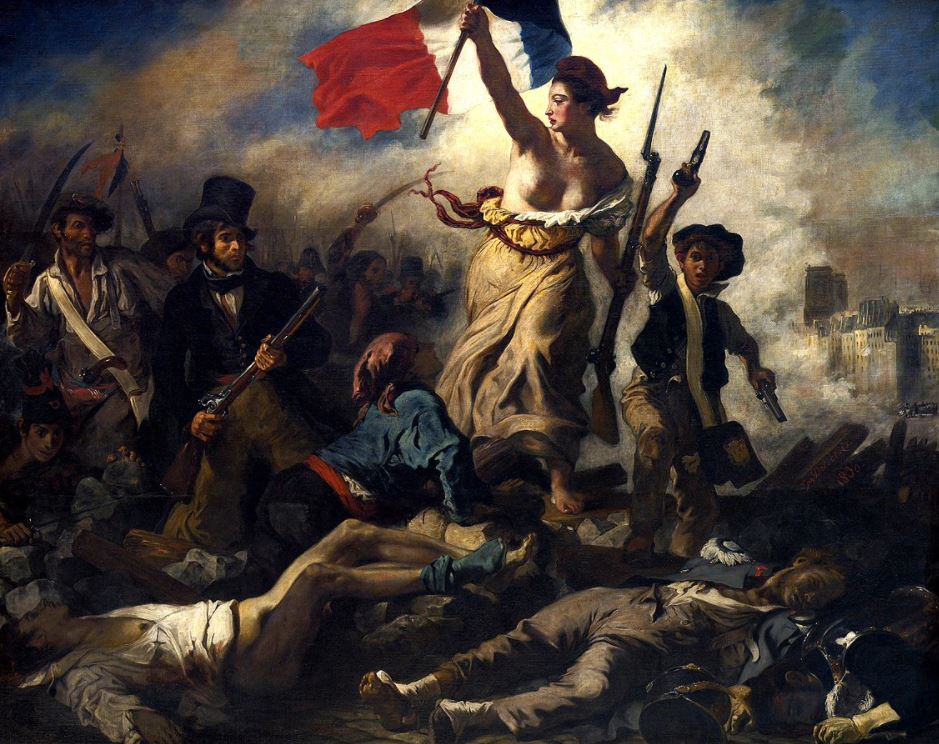
- Liberty Leading the People (1830) – A monumental painting by Eugène Delacroix that commemorates the July Revolution of 1830 and which depicts Marianne, the personification of the French Republic, in all her glory.
- The Fighting Téméraire (1839) – A distinctive painting by Joseph Mallord William Turner that depicts a battleship being towed to its final destination.
If you want to discover more Romantic artworks, check out some of these amazing Romantic paintings!