Historical and mythological paintings were not interesting for Édouard Manet (1832-1883), a renowned French artist who played a major role in the development of modern art.
He was one of the first artists in history who depicted life as it really was, and especially anything related to leisure was his cup of tea.
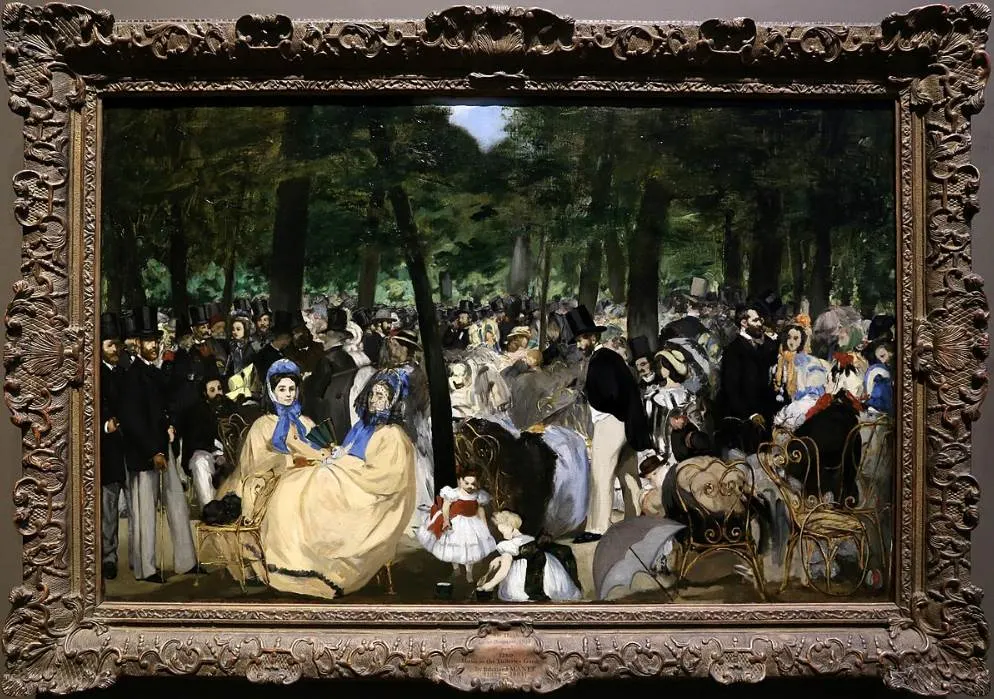
In this article, we take a closer look at some of the most interesting facts about Music in the Tuileries by Édouard Manet, a masterpiece by the artist who formed the bridge between Realism and Impressionist artists.
1. The painting was completed in the early 1860s
Édouard Manet was born and raised in Paris and his family was extremely well off. His father was a judge who wished that his son would pursue a career in law.
When it became clear that he had a talent for painting, his father reluctantly agreed that he could pursue an artistic career in the early 1850s.
Like most young artists, he received academic training and started copying masterpieces at the Louvre, mainly works from the Old Masters.
When he opened his studio in 1856, he adopted the style of Realism artists such as Gustave Courbet (1819-1877) and focused on depicting people from the lower class.
He completed one of his first major paintings titled Music in the Tuileries about 6 years later in 1862.

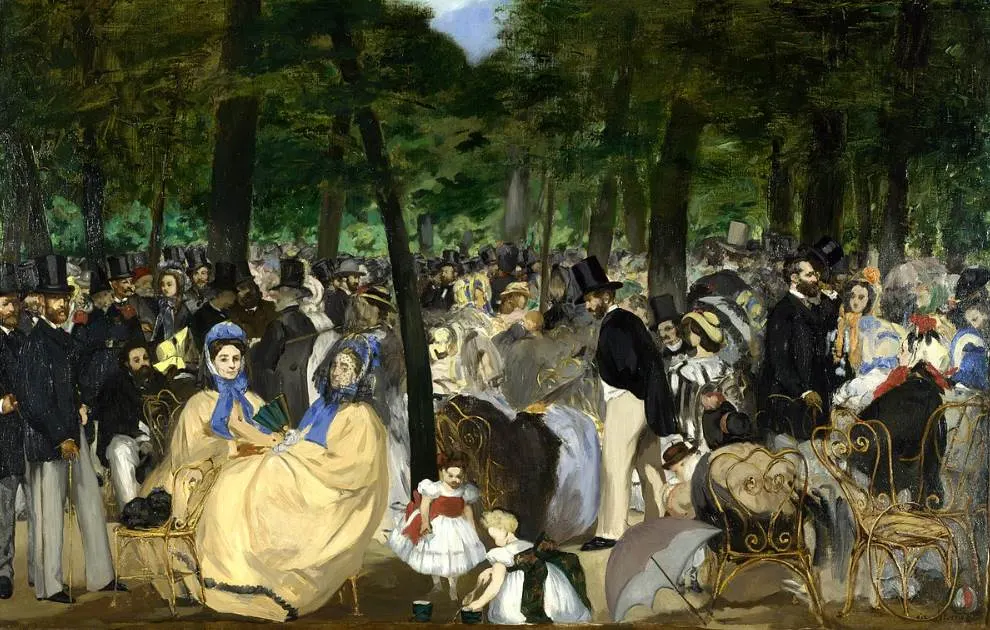
2. It depicts Parisians who are having a good time in a public park
As the name of the painting suggests, the painting depicts a large number of people who are spending a Sunday afternoon at the Tuileries Garden.

This public park is located in between the Place de la Concorde and the Louvre in the heart of Paris and has been a public place to hang out since the 19th century.
This was a period shortly after Napoleon III came to power (he reigned ad French Emperor between 1852 ad 1870), and the Emperor made some serious changes to the park so concerts could be held here.
We can’t see the musicians, but the way Manet depicted the scene makes it easy to imagine the ambiance inside this crowded park.

3. The painting depicts a forested area near the Louvre Museum
The Tuileries Garden was still enclosed by Louvre Museum and the Tuileries Palace at the time. Less than a decade later, the Tuileries Palace was destroyed during the Paris Commune in 1871.
The concert location was near the Louvre Museum, not too far from the Arc du Triomphe du Carrousel. This arch was constructed in 1809 by Napoleon Bonaparte to celebrate his victories.
This is the section that was once enclosed by the two palaces and which was open to the public for fashionable Parisians to have a good time during the Summer months.

4. Both the painting’s technique and subject matter were revolutionary at the time
Manet had easy access to the Louvre Museum and started his career copying some of the most famous artists in history.
He was especially fond of Dutch artist Frans Hals, one of the greatest portrait painters of the Dutch Golden Age, and Spanish artist Diego Velázquez (1599-1660).
His first notable painting, “The Spanish Singer” (1860) can be described as an ode to the paintings of the Spanish artist whom he admired so much.
The French artist started experimenting with both new subject matter and a new painterly painting technique that would revolutionize the world of art in the second half of the 19th century.
His technique is easily recognizable. This work along with his famous “The Luncheon on the Grass” (1863) is considered to be some of the first examples of modern art.

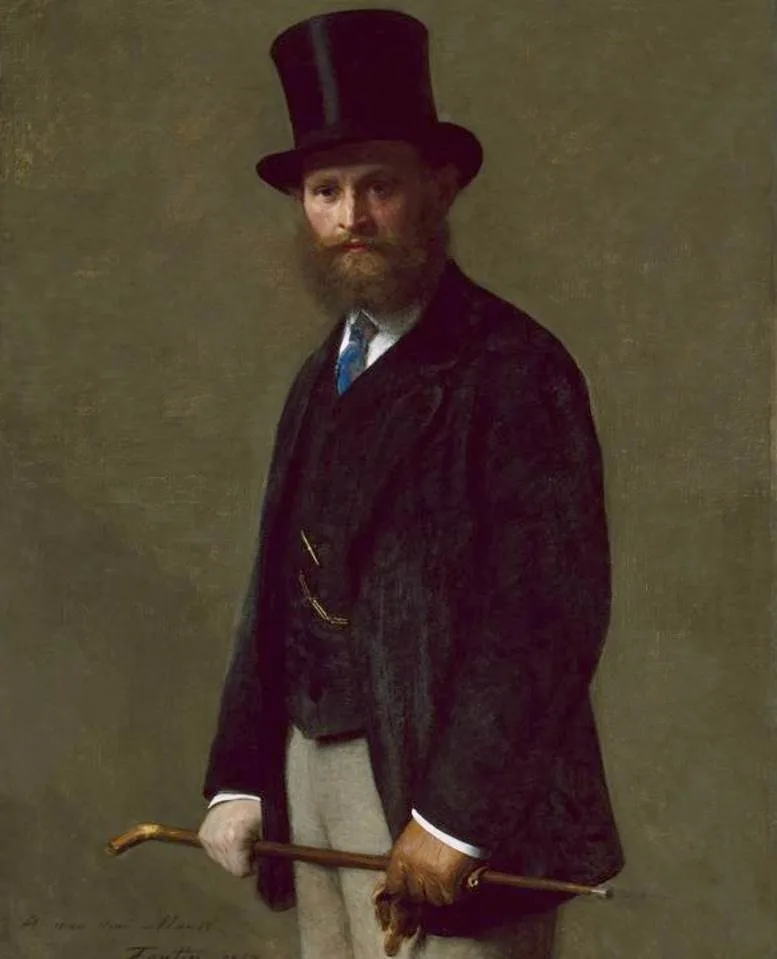
5. Manet included himself and his brother Eugène in the painting
Manet included several people he knew, including artists, authors, and musicians. He also painted a self-portrait in the utmost left part of the painting.
The man in the bottom right corner of the image below is a sculptor and art critic named Zacharie Astruc.
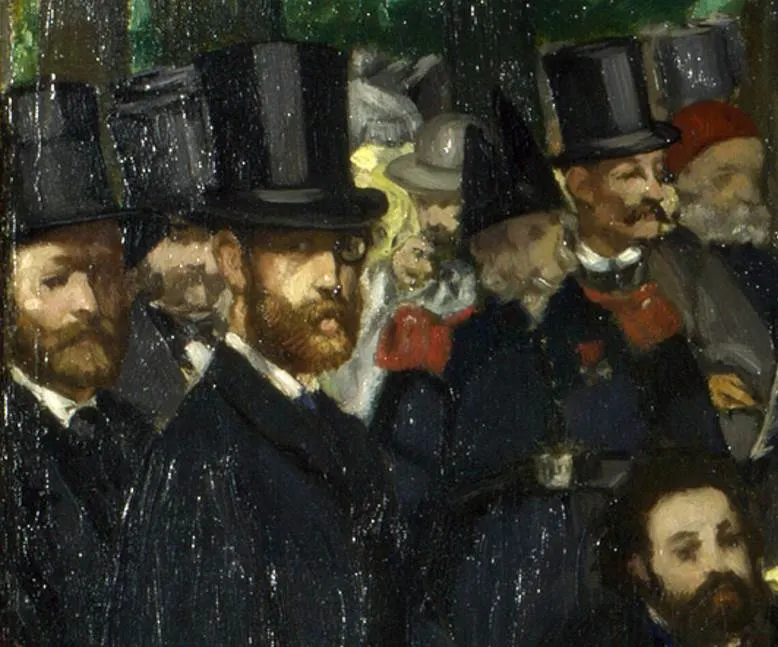
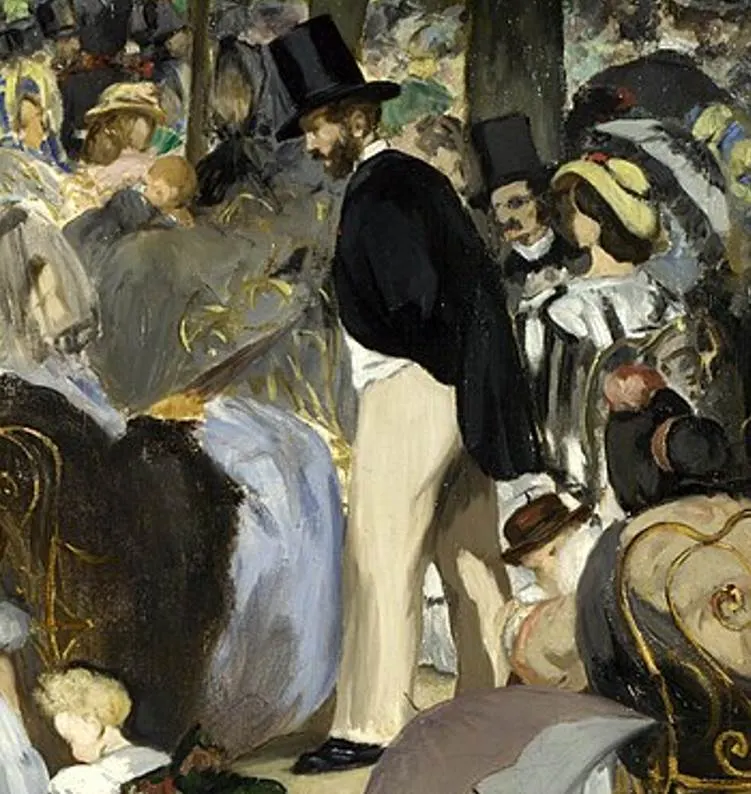
The other notable person that is easily recognizable is the man dressed in cream trousers who is standing in the foreground.
He is identified as Eugène Manet (1833-1892), the artist’s brother and husband of renowned Impressionist artist Berthe Morisot (1841-1895). He never achieved the fame of his brother and mainly supported his wife’s successful career.

6. The painting inspired other artists to produce similar works of art
The significance of Music in the Tuileries in the history of art can’t be underestimated. It was the first example of a painting that depicts an outdoor urban scene of this scope.
It’s also a predecessor of Impressionist paintings as it depicts the scene as Manet perceived it as opposed to an exact representation of the event that would be present in a Realism painting.
Because of this, the painting received a lot of criticism and as even described as being unfinished by some art critics when it was first exhibited in 1863.
It inspired multiple artists of future generations to produce similar works. For example, “Dance at Le Moulin de la Galette” (1876) by Pierre-Auguste Renoir is considered to be one of the most famous Impressionist paintings in history.
Why was Music in the Tuileries so controversial at the time? French journalist Emile Zola perfectly summarized this feeling by saying:
We are not accustomed to seeing such simple and direct translations of reality.

7. How big is Music in the Tuileries by Édouard Manet?
Despite the importance of the painting, this work is far from being the largest painting in his oeuvre.
Music in the Tuileries by Édouard Manet is a medium-sized oil on canvas painting that has dimensions of 76 × 118 centimeters (30 × 46 inches).

8. Where is the painting located today?
The painting remained in the artist’s collection until 1883 when he managed to sell it to opera singer and art collector Jean-Baptiste Faure.
It was subsequently acquired by renowned French art dealer Paul Durand-Ruel in 1898. He sold it to Irish art collector Sir Hugh Lane (1875-1915) in 1903.
Lane established the museum known today as the Hgh Lane Gallery in Dublin in 1908.
It was scheduled to enter the gallery’s collection following Lane’s death on board of the RMS Lusitania in 1915. A legal battle between the National Gallery in London and the museum in Dublin only revolved in a compromise in 1959.
The painting is now co-owned by both museums and is currently on display at Hugh Lane Gallery in Dublin.

