One of the most influential Flemish artists of the first 3 decades of the 17th century was an extremely versatile painter named Jan Brueghel the Elder (1568-1625). He collaborated with his good friend, Peter Paul Rubens (1577-1640), on many notable works of art.
This renowned Mannerist artist eventually became the court painter of the Habsburg rulers in the Habsburg Netherlands and he earned himself several nicknames along the way.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the most interesting facts about this talented individual who was born to become a famous artist.
1. He was the son of a famous Renaissance artist
Jan Brueghel the Elder was born in Brussels in the year 1568. He was the son of Pieter Bruegel the Elder (1525-1569), one of the most renowned Renaissance artists in the Low Countries.
It’s fair to conclude that he was born to become a great artist himself, not just because of his father, but also from his mother’s side. She was the daughter of a Flemish polymath named Pieter Coecke van Aelst, a man proficient in painting, sculpting, and architecture.
Jan had an older brother named Pieter Brueghel the Younger (1564-1638) who became a famous artist in Antwerp as well.
2. Both Jan and his brother were taught by their grandmother
His father passed away when Jan was only 1 year old, and his mother died relatively early as well in the year 1578. It’s believed that both brothers and their sister Marie were supported by their grandmother named Mayken Verhulst.
An artist in her own right, the woman is believed to have been the first tutor of the two young brothers as she showed them how to draw and use watercolor to paint. During their teenage years, they were sent from Brussels to Antwerp to study oil painting.
Yes, the Brueghels’ were raised to become great artists and that’s exactly what they became.

3. He lived in Rome for 2 years between 1592 and 1594
Many Flemish and Dutch artists visited Italy to increase their knowledge about painting and sculpture. Jan Brueghel the Elder first stayed a while with his sister Marie who lived in Cologne in Germany before departing to Naples and possibly Venice in the year 1590.
He completed multiple works for his patron in Naples, a man named Don Francesco Caracciolo, before settling in Rome between 1592 and 1594.
It’s in Rome that he learned about all aspects of the Catholic Counter-Reformation of the 16th century, a subject that would dominate many of his future paintings.
He followed his patron in Rome, Cardinal Federico Borromeo, to Milan when the man became the Archbishop of this city, producing many religious paintings in the process.
4. He spent most of his artistic career in Antwerp
After spending about 6 years in Italy, it was time for the Flemish artist to return home. He was considered to be a master with international experience in the late 16th century and entered the prestigious Guild of Saint Luke in Antwerp.
This also meant that he could establish his workshop as an independent master. He also married a woman named Isabella de Jode in 1599 and the couple had 2 children, a son named Jan Brueghel and a daughter named Paschasia Brueghel.
unfortunately, the marriage was cut short by the sudden passing of his wife in 1603, the same year that their daughter was born. Both events might be related to each other as well.

5. Brueghel got 3 nicknamed referring to his artworks
Apart from a brief visit to Prague in 1604 where he developed his remarkable Mannerist style, he mainly lived and worked in Antwerp. He became the court painter of Archduke and Duchess Albrecht and Isabella in 1606, the governors of the Habsburg Netherlands at that time.
During his career, he created a wide variety of paintings, including mythological scenes, landscapes, seascapes, hunting scenes, still lifes of flowers, religious paintings, portraits, and battle scenes.
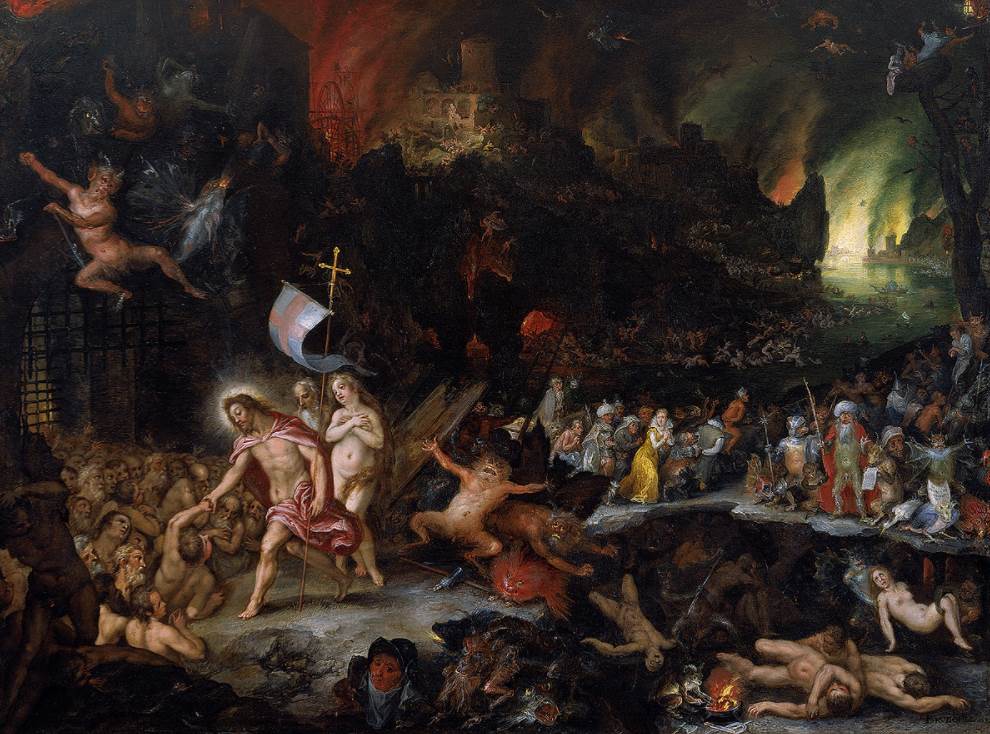
He was also an innovative artist who invented several new themes, including flower garland paintings, gallery paintings, and paradise landscape paintings. His religious works were mostly inspired by the Catholic Counter-Reformation, and he has several works depicting the underworld in his name as well.
Because of his versatile nature in terms of subjects, just one nickname didn’t do. That’s why he was referred to as:
- Velvet Brueghel – A reference to the materials he used to prepare his works.
- Flower Brueghel – A reference to the numerous flower still lifes he produced.
- Paradise Brueghel – A reference to the invention of “paradise landscapes” he is credited with.
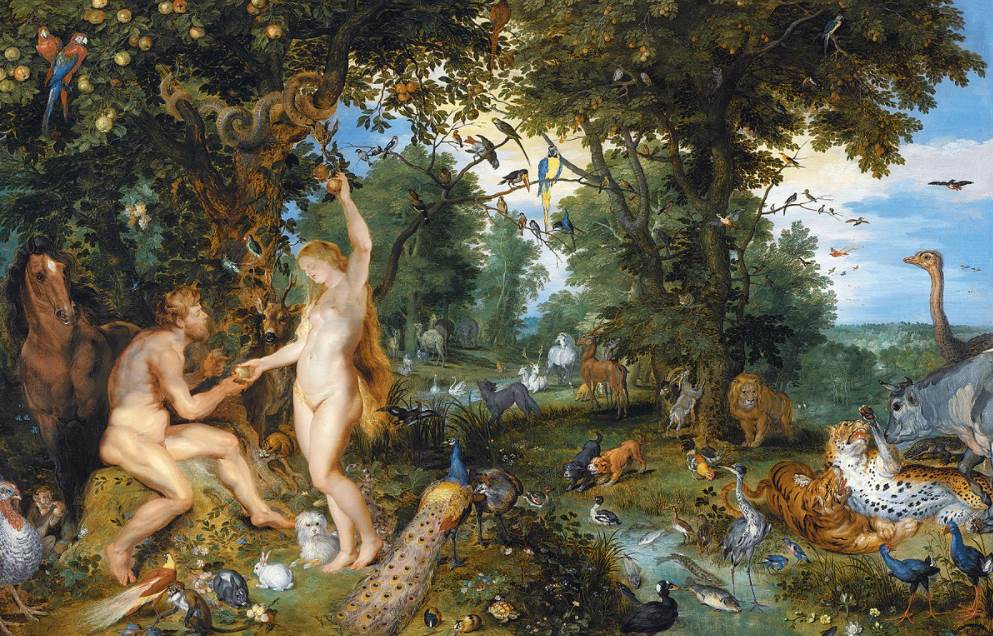

More interesting facts about Jan Brueghel the Elder
6. Most of his works are defined by the extreme level of accuracy that he was able to integrate into his paintings. This is especially true when it comes to his landscapes and depictions of nature and animals.
This also means that he wasn’t commissioned with monumental works of art for local churches such as the paintings by Rubens for example. His clientele was the members of the aristocracy and rich collectors of fine art.
7. Jan Brueghel the Elder was a lifelong friend of Peter Paul Rubens, a man who was the godfather of the two children with his first wife. Following the devastating loss of his wife, he bought a mansion in Antwerp called “De Meerminne” (The Mermaid).
He remarried pretty fast as well in April of the year 1605. His second wife was a woman named Catharina van Mariënburg and the couple had 8 children together.
8. Before he remarried, he spent some time visiting Prague, an important center in the world of art in the early 17th century. This was due to the court of Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, who was an important patron of the arts.
It’s here that the transition between the Renaissance artists and Mannerist artists emerged, a trend that continued and which eventually inspired Baroque artists such as Rubens who exaggerated dramatic effects into their works.
9. Just like his friend Rubens, the workshop of Jan Brueghel the Elder grew quickly which allowed him to produce paintings on a mass scale. This also means that most of his famous paintings were reproduced multiple times.
10. His brother was nicknamed “Hell Brueghel,” a reference to the scenes of the underworld featuring fire and devils that were once attributed to him.
A closer examination of these works has concluded that it was his brother Jan who completed these, which means that the 4th nickname of Jan Brueghel the Elder is actually “Hell Brueghel.”

